Fibroids
What are fibroids?
Fibroids, medically known as uterine leiomyomas, are non-cancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They are the most common benign tumours of the female reproductive system, occurring in 20-30% of females, most often in women aged 30-50.
While generally harmless, fibroids can cause discomfort and impact reproductive health depending on their size and location, making awareness and timely management crucial.
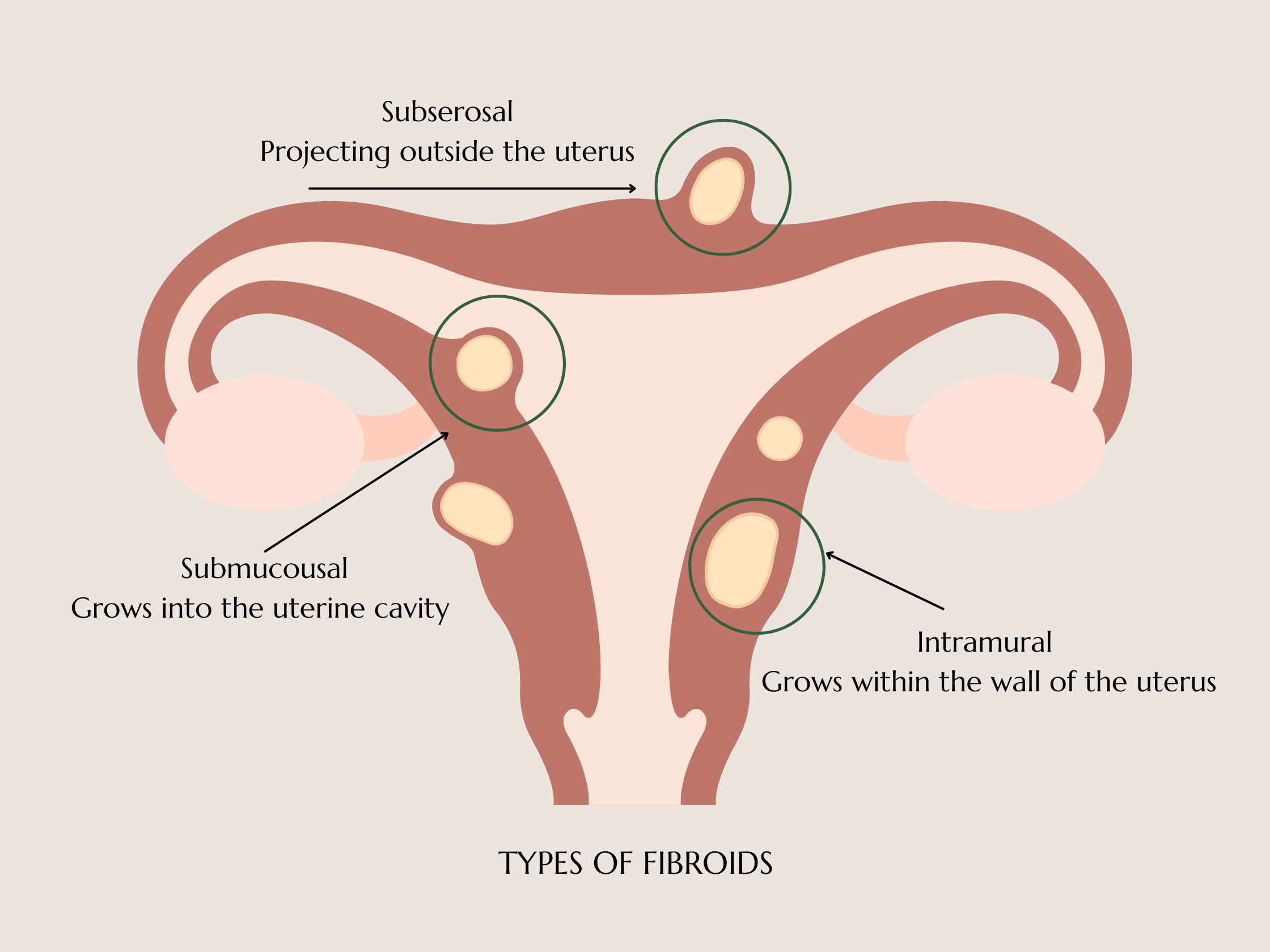
Types Of Fibroids
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or on the uterus, and they can vary widely in size, number, and location. Understanding the types of fibroids is important because their classification can directly influence both diagnosis and treatment options.
The uterine fibroid classification generally depends on the location of fibroids in the uterus.
Intramural Fibroids
Intramural fibroids are the most common type, growing within the muscular wall of the uterus. They can cause symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, and low back pain.
Subserosal Fibroids
Subserosal fibroids develop just beneath the outer lining of the uterus and can grow large enough to extend into the pelvis. They often cause fibroids symptoms such as pressure on the bladder or bowel, leading to frequent urination or constipation.
Submucosal Fibroids
This type of fibroid grows just beneath the inner lining of the uterus. They can cause heavy, prolonged, or irregular menstrual bleeding, blood clots during periods, and anemia from excessive blood loss. In some cases, they may also contribute to fertility problems or recurrent pregnancy loss.
Pedunculated Fibroids
Pedunculated fibroids are attached to the uterus by a stalk, often resembling a mushroom. They can cause pelvic pressure or discomfort, and sudden sharp pain if the stalk twists.
Through thorough evaluation and imaging, a gynaecologist can determine the exact fibroid type one may have and recommend the best treatment option.
Symptoms
Many women who have this condition are not aware of it as most do not experience symptoms. However, some may experience the following:
- Heavy/painful, long-lasting periods
- Abdominal pain
- Lower back pain
- A need to urinate
- Constipation
- Pain/discomfort during sex
Complications
In rare cases, complications may arise due to the size and location of the tumour, such as:
- Infertility
- Difficulties during labour/ after birth
- Preterm birth
- Miscarriage
When should I see a doctor?
See your doctor if you have:
- Pelvic pain
- Heavy periods
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Difficulty getting pregnant
What will the doctor do during consultations?
Here are some things you can expect from our gynaecologists at Eden Women’s Health:
- History taking of symptoms and general health
- Initial screening for fibroids using ultrasound and associated investigations
- Discussion of treatment options
- Scheduling of a hysteroscopy/ laparoscopy if needed
Why Choose Eden Women’s Health
At Eden Women’s Health, we provide expert care for every patient with a compassionate, personalised approach. Our team combines modern technology with a supportive environment to ensure you feel informed, comfortable, and confident in your care.
- Experienced Gynaecologists: Skilled specialists in diagnosing and treating fibroids.
- Accurate Diagnostics: Ultrasound and imaging ensure accurate detection and assessment.
- Minimally Invasive Options: Effective treatments designed to reduce recovery time and minimise discomfort.
- Personalised Treatment Plans: Care tailored to your unique needs, symptoms, and reproductive goals.
- Patient-Centered Care: Supportive, compassionate guidance for your wellness.
With our team, compassionate care and personalised treatment go hand in hand, so you always feel understood and supported.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can fibroids affect my fertility?
Yes, fibroids can impact a woman’s fertility and pregnancy outcomes. Submucosal fibroids, in particular, may interfere with implantation or block a fallopian tube, making it more difficult to conceive.
2. Will fibroids go away on their own?
Small fibroids may shrink or disappear naturally, often when estrogen levels drop, such as during menopause. However, this happens in only about 10% of cases. Fibroid size, location, and individual factors all play a role, so it’s important to consult a specialist.
3. What’s the recovery time for fibroid surgery?
Recovery time depends on the type of procedure, but generally it can be as long as 6–8 weeks for major surgeries like an open hysterectomy or myomectomy.
4. Can fibroids return after treatment?
Yes, new fibroids can redevelop over time due to genetics, hormone imbalances, and various lifestyle factors.
5. Are fibroids cancerous?
No, fibroids (uterine leiomyomas) are non-cancerous growths and are the most common benign tumors of the female reproductive system.

Schedule An Appointment
Living with fibroids should not mean compromising your well-being or reproductive goals. Schedule a consultation with us today and take the first step towards optimal reproductive health and wellness.

